Is the Universe Expanding Faster than Light? Understanding the Concept
Written on
Chapter 1: The Nature of Universal Expansion
Is it accurate to claim that the Universe's space is expanding at a rate exceeding that of light? This intriguing question came from one of my subscribers.
To assert that space is outpacing the speed of light isn't entirely precise. Space itself is not moving; instead, new space is constantly being generated, which leads to an increase in distance between objects. This phenomenon creates the illusion of objects drifting apart.
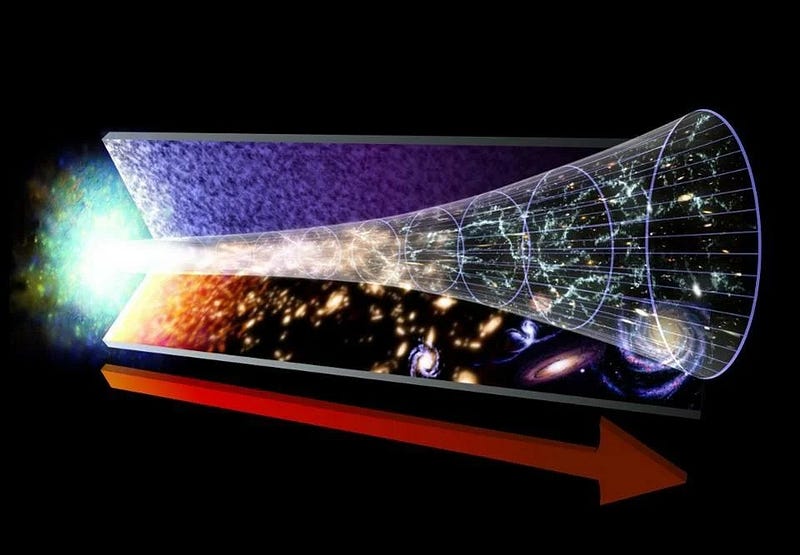
The light-speed limit applies strictly to the movement of objects within the Universe, not to the apparent motion we observe. We can only see objects moving away from us at speeds below the speed of light. However, it's possible that some objects beyond the cosmic event horizon are receding at superluminal speeds, and we will never be able to gather information from these distant entities.
Moreover, while the speed of light constrains the transmission of information, it does not prevent the superluminal movement of objects that are causally disconnected. In this context, Einstein's general relativity governs events within the event horizon, but it places no restrictions on the realm beyond it.
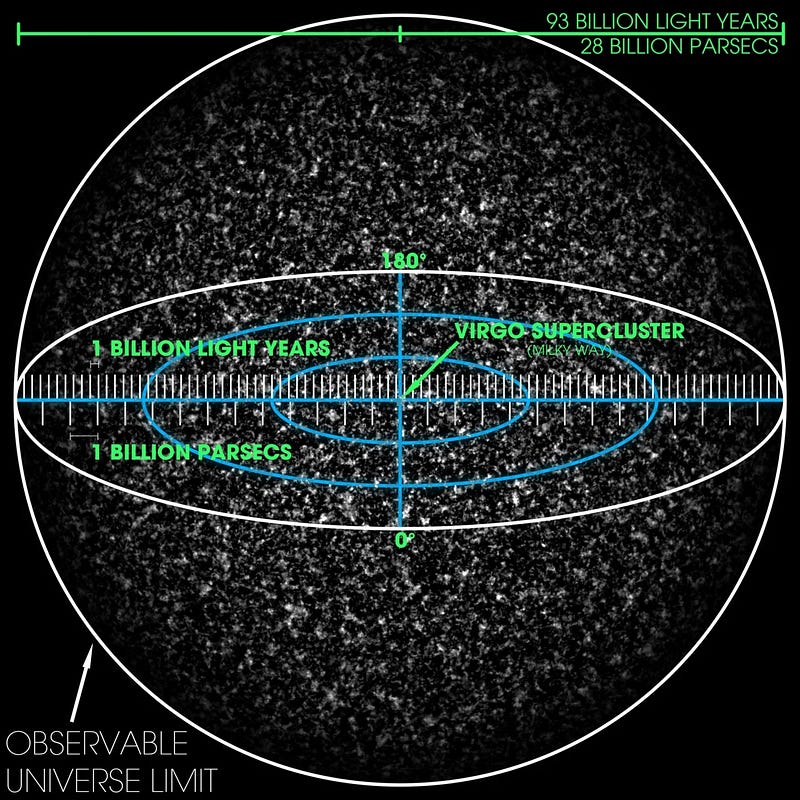
Read more: Five Alternatives to the Big Bang Theory
Essentially, it's impossible to definitively state that the Universe is expanding at a uniform rate. Different galaxies are receding from one another at varying velocities, in accordance with Hubble’s law.
If you're interested in more articles about space, give this a clap! Don’t forget to subscribe to our channel, and feel free to pose your questions, which I will address in future articles. If you appreciate my work, consider supporting me by joining Medium for just $5 a month, enabling us to produce even better content.
Chapter 2: The Cosmic Illusion of Speed
This video explores whether the Universe is expanding faster than light, delving into concepts of cosmology and astrophysics.
In this video, we discuss the implications of the Universe's expansion and how it relates to the speed of light and our understanding of cosmic phenomena.