Understanding Covid-19: The Logistic Function's Role
Written on
Chapter 1: The Dynamics of Exponential Growth
The phenomenon of exponential growth can be illustrated through the human body’s response to extreme temperature increases. When a person's temperature exceeds 42°C, the body enters a perilous cycle. Positive feedback loops accelerate metabolic processes, which further raise the temperature, leading to cellular damage and ultimately, death.
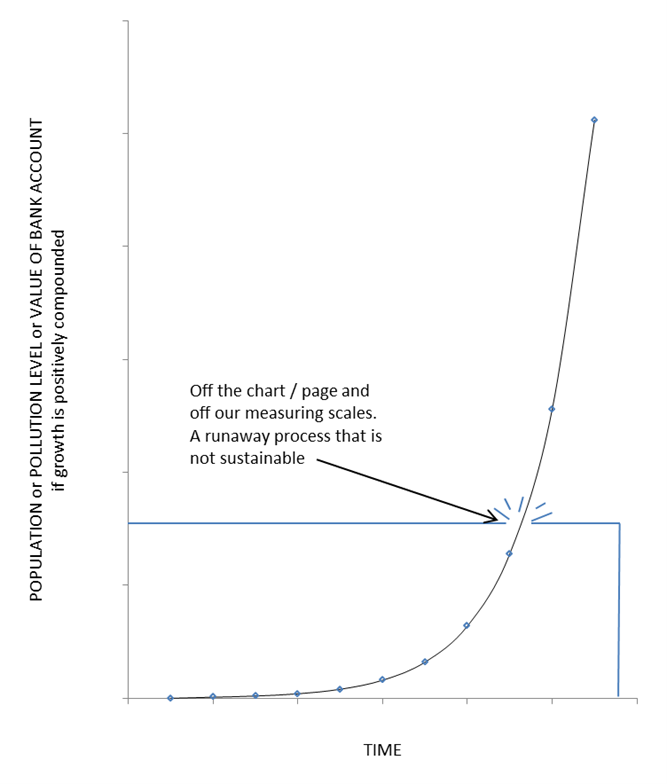
Garrett Hardin, in his work “Living Within Limits,” sheds light on this “runaway” effect, equating it to the concept of exponential growth in finances. He emphasizes that such unchecked growth is unsustainable, as illustrated in the accompanying graph. Aspects like population, pollution, or Covid-19 infections, if they continue to grow exponentially, will eventually surpass our capacity to measure or manage them.
Section 1.1: The Concept of Logistic Growth
In the real world, exponential growth is eventually curtailed by limits known as the “carrying capacity” of an ecosystem. Pierre-Francois Verhulst, a Belgian mathematician, was the first to articulate a mathematical function that acknowledged this limitation while examining Thomas Malthus' theories on population dynamics. Malthus suggested that population growth follows an exponential pattern, whereas food production increases arithmetically. He warned that this discrepancy would inevitably lead to resource shortages, resulting in crises such as disease and famine.
Verhulst's logistic function is a mathematical model that captures this initial exponential growth followed by a plateau as resources become scarce.
The logistic function serves as a framework to understand the ongoing struggle between humans and the SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for Covid-19. If left unchecked, the virus would infect and claim countless lives until reaching a saturation point. This saturation could lead to a coexistence scenario, where the virus continues to exist among humans, or it could eventually diminish after causing significant fatalities.
Section 1.2: Historical Context of Viral Threats
A poignant example of a historically devastating virus is smallpox, which has plagued humanity for centuries. Evidence of its deadly impact can be traced back 2,300 years in Egyptian mummies. Richard Preston, in his introduction to D.A. Henderson's work on smallpox eradication, notes that the virus is believed to have killed approximately half a billion people in its last century of existence. Despite early inoculation methods developed in China during the 1500s, it wasn’t until Edward Jenner's vaccine in 1796 that real progress was made. Yet, it took another 184 years and a massive global vaccination effort to eradicate smallpox in 1980.
While Covid-19 and smallpox differ significantly, particularly in terms of mortality rates, the lessons learned from smallpox remain relevant today. As of November 21, 2020, Covid-19 had claimed 1.37 million lives globally, with many effects still poorly understood.
Chapter 2: The Challenge of Ideological Viruses
The hurdles we face are formidable. A particularly daunting obstacle is the blend of dogma and triviality that has permeated societies worldwide. Richard Dawkins, an evolutionary biologist, refers to these harmful ideologies as “Viruses of the Mind.” Similar to biological viruses, these ideas proliferate through populations, following a logistic pattern.
To mitigate the threat posed by the SARS-CoV-2 virus and others, we must embrace critical health practices such as wearing masks, practicing social distancing, and maintaining hygiene. These measures can help slow the virus's spread and allow society to reach a stable equilibrium. Without them, the number of infections could rise dramatically, delaying the point at which the virus's growth stabilizes. Even with vaccines becoming available, achieving widespread immunization will be a lengthy process, complicated by anti-vaccination sentiments and logistical challenges.
Section 2.1: Cultural Decline and Knowledge Erosion
In “The Swerve,” Stephen Greenblatt discusses the decline of the Roman Empire in the 5th century, when dogma overshadowed genuine learning. He describes this period as one marked by a “loss of cultural moorings,” leading to a descent into febrile triviality. In our current era, dominated by social media and binge-watching, we must question whether we are experiencing a similar decline in critical thought.
We Have a Choice
Verhulst, who introduced the logistic function, was acutely aware of the socio-political climate in early 19th-century Europe. During a visit to Rome in 1830, he became inspired by revolutionary events and drafted a democratic constitution for the Vatican, only to be expelled by the authorities.
Although Verhulst passed away at a young age, his logistic function continues to serve as a vital analytical tool. The responsibility to heed its warnings lies with us.