Understanding the Evolution of Global Energy Consumption
Written on
Chapter 1: The Historical Energy Landscape
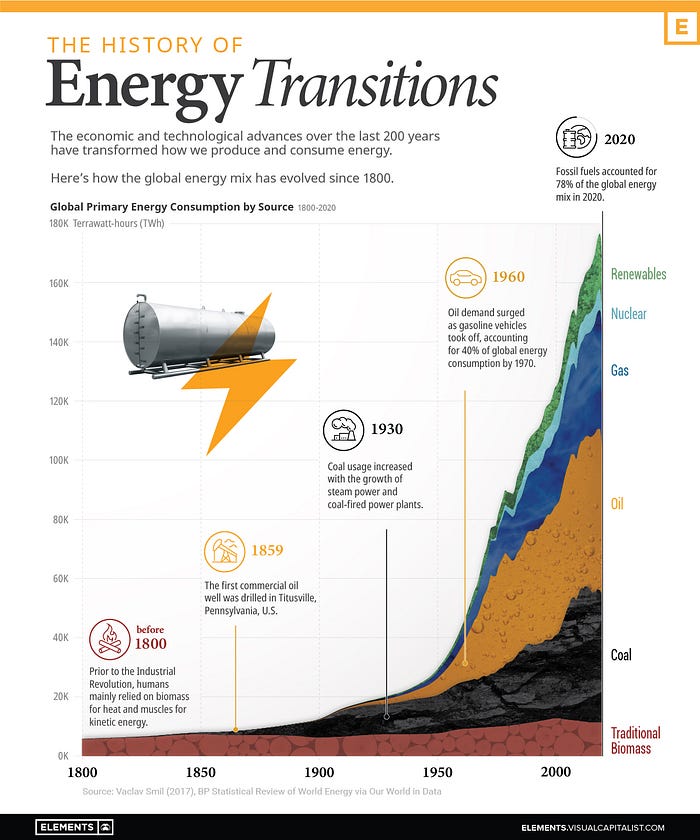
The global energy landscape has experienced significant transformation over the last two centuries, primarily driven by advancements in technology and economics. Two pivotal shifts in energy production and consumption have shaped this evolution since the year 1800. The first shift occurred in the latter half of the 19th century, as economies transitioned from an agrarian focus to a more industrialized framework. The second shift emerged during the latter half of the 20th century, characterized by a diversification in the energy mix.
The accompanying infographic provides a historical overview of these changes, illustrating the movement toward a more sustainable energy model, moving away from a fossil fuel-dominated system. The data for this visualization is sourced from Our World in Data.
In the current energy mix, we observe the presence of coal, oil, gas, nuclear power, hydropower, solar energy, wind energy, and biofuels. In contrast, the early 1800s presented a much simpler energy landscape, where people relied heavily on solid fuels like wood, crop waste, and charcoal for heating and other essential needs. As economies advanced and demands for more efficient fuel alternatives increased, coal became a significant player in the energy narrative.
With the industrial revolution in the late 19th century, coal usage surged, primarily fueled by steam engines that were dependent on this resource. The contribution of coal to the energy mix escalated from a mere 1.7% in 1800 to a staggering 47.2% by 1900.
Although oil was discovered in the late 19th century, its application was largely limited to lighting lamps. It wasn't until the advent of mass-produced automobiles in the early 20th century that oil consumption became widespread. The introduction of assembly line production and the post-World War II boom in the aviation industry further propelled oil's prominence.
The invention of the Bunsen burner marked a turning point, paving the way for increased gas usage in homes. With the establishment of pipeline infrastructure, gas became a common source for heating, cooking, and powering water heaters, gradually replacing coal in the residential sector. This shift saw coal losing its foothold in both the home heating market and transportation, where oil had taken precedence.
Nuclear energy made its debut in the energy mix in the 1960s, while renewable sources like solar and wind were introduced much later, in the 1980s. In recent years, renewable energy sources have gained significant attention as the world strives for a more sustainable energy future. This transition is motivated by urgent climate goals, particularly the target of achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
Despite renewables comprising only 3.5% of the total energy mix a decade ago, their adoption is accelerating. However, the challenge of phasing out fossil fuels within the next 30 years remains monumental, requiring an unprecedented scale and speed of transition. A shift toward a fully renewable energy system will demand substantial investments in infrastructure and grid storage, as well as significant changes in energy consumption behaviors. Most importantly, political will is essential to drive this transformation.
Section 1.1: Global Energy Consumption Over Time
This section delves deeper into the historical trends of global energy consumption and production, providing insights into key developments.
The first video, "Global energy consumption by source from 1800 to present," visually depicts the evolution of energy sources throughout history, illustrating the shifts in consumption patterns.
Section 1.2: The Rise of Renewable Energy
As we progress into the 21st century, renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly vital. This section explores the growth of renewables and their impact on the global energy landscape.
The second video, "Winner: Best Scientific Visualization SC19; Primary energy source of life from Birth of Planet Earth," offers a captivating visualization of energy sources over the ages, emphasizing the journey toward sustainable energy.